Key Natural Resource Issues in Conservation Halton’s Watersheds
Conservation Halton has identified 13 key natural resource issues and risks that will be addressed in our 2024 Watershed-Based Resource Management Strategy (“Watershed Strategy”). These issues and risks were identified in the context of climate change and based on a review of environmental monitoring data, technical reports/studies, a public survey, and the expertise of Conservation Halton’s staff.
Background Information
This section explains the causes of natural resource issues in Conservation Halton’s watersheds.
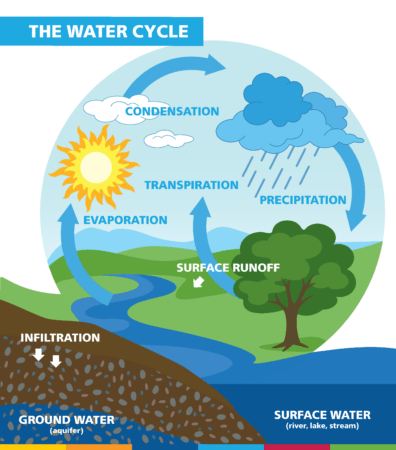
Water is vital. It supports all life on earth and connects natural features, plants, animals, and human beings that rely on it. Precipitation, evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing are important parts of a continuous cycle. Within our local watersheds, some precipitation infiltrates into the ground. Some of it flows along the surface of the land and enters creeks, wetlands, and the lake as runoff. Water evaporates from the plants, animals, land, and waterbodies, helped by the sun. Evaporated air, as moisture, is carried up into the atmosphere; it condenses to form clouds, then falls once again back to earth as precipitation. It continually moves in an integrated system called the hydrologic cycle, also known as the water cycle. Understanding the connections and influences of natural processes and human activities on the water cycle is critical to identifying and managing natural resource issues.
The water cycle has natural variability (e.g., periods of droughts and floods). However, human activities have led to profound changes in the water cycle. Converting land from its natural state, such as cropping or urbanization changes the way water moves over the landscape. Hardened surfaces such as concrete and pavement reduce the ability of the land to infiltrate water into the soil, increasing and accelerating contaminated surface runoff. Dams, weirs, channels, and other structures alter the flow and direction of water through a watershed. Taking water from surface and groundwater sources can also alter its natural pathways, reduce downstream flow, deplete groundwater levels, and influence water availability to springs and wetlands. Human activities — particularly the burning of fossil fuels, land clearing and urbanization — are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and warming the planet. Rising temperatures cause the rates of evaporation and precipitation to intensify.
A changing water cycle increases the frequency and intensity of natural hazards such as drought, extreme heat and precipitation events globally and in Conservation Halton’s watersheds. Simply put, our future climate will be warmer, wetter and wilder. We are already experiencing an increase in the frequency and severity of localized weather events, such as heat waves, heavy rainfall, ice storms, and heavy winds. These extreme weather events affect biodiversity and pose risks to human health, safety, and property.
Summary of Key Natural Resource Issues
Conservation Halton has identified 13 key watershed-scale natural resource issues and risks specific to our watersheds. Other natural resource issues in our watersheds are more localized, but no less important to address. These issues include dynamic beaches, shoreline erosion, shoreline flooding, surface/overland erosion, unstable bedrock (e.g., karst), and unstable soils.
Description: Flooding occurs when water overtops the banks of creeks and flows onto adjacent lands. Flooding results from intense rainfall over short periods of time, long periods of rainfall, heavy snow melt, or channel constrictions such as ice jams, debris, or undersized infrastructure. Other factors can worsen flood risk including the loss or degradation of natural features such as wetlands, increased impermeability of soils due to urbanization, illegal dumping of fill in creek valleys, physical alterations to creek banks which may cause waters to spill beyond the natural floodplain, and climate change.
Conservation Halton maps flood hazards according to provincial standards.
| HISTORIC FLOODING | VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Drought occurs when there is a water shortage. It results from a period of persistent drier-than-normal conditions with below normal precipitation and high temperatures. Other factors that can worsen drought include the loss and fragmentation of forests and wetlands, an increase in the use of surface and groundwater, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors drought through our Low Water Response Program.
| HISTORIC DROUGHTS | VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Valley erosion occurs when there is an excessive loss of soil due to natural creek processes. Valley erosion results from periodic increases in peak creek flow, changes in channel form, unstable and steep slopes, loss of riparian vegetation (a strip of vegetation along the edge of a creek or waterbody), sediment load levels, ice jams or soil type. This can cause bank slumping, scouring, undercutting, and ultimately slope failure. Other factors can worsen valley erosion including vegetation removal, construction activities in proximity to the slope (e.g., illegal dumping or excavation of fill in creek valleys, soil compaction, inadequate drainage, and new structures), poorly maintained infrastructure such as culverts and bridges, and climate change.
Conservation Halton maps valley erosion hazards according to provincial standards.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Chloride is released through natural processes such as bedrock weathering and precipitation. There have been significant increases in chloride concentrations in surface water over the last 50 years throughout the watershed. At least one sample taken from most monitoring sites over a recent five-year period exceeds the provincial guideline (e.g., Fourteen Mile Creek at Lakeshore Rd, Oakville; Sixteen Mile Creek Main Branch at Speers Rd; and Sheldon Creek at Shell Park, Oakville). Other factors can increase chloride concentrations including use of road salt and water softening salt, degraded and/or loss of natural features that filter water, stormwater management ponds, and wastewater treatment plant effluent.
Conservation Halton monitors chloride concentrations in surface water and ground water as part of the Provincial Water Quality Monitoring Network, and through our surface and groundwater water quality monitoring programs.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Suspended solids are materials such as silt, clay, plankton, and microscopic organisms that remain suspended in the water column. They typically carry pollutants and nutrients. Concentrations are variable throughout the watersheds depending on weather conditions (e.g., high during storm events and low during dry periods) and are influenced by erosion and the decomposition rate of organic materials. Other factors can increase suspended solids concentrations including loss of riparian vegetation, runoff from urban and agricultural areas, illegal dumping of fill in creek valleys, wastewater treatment plant effluent, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors suspended solids concentrations in surface water as part of the Provincial Water Quality Monitoring Network and through our surface water quality monitoring program.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Sedimentation occurs when solid particles settle out of suspension to the creek or pond bottom. Factors that increase sedimentation include runoff from poorly managed fields and construction sites with inadequate erosion and sediment controls, illegal dumping of fill in creek valleys, dams, weirs, and climate change.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Phosphorus is a nutrient released into the environment naturally through bedrock weathering and erosion processes. It binds to suspended sediment and causes increased plant growth, including algae. Total phosphorus is a measure of all phosphorus, whether dissolved or particulate. Average annual concentrations have exceeded the provincial guideline at almost all the watershed monitoring sites at least one year over a recent five-year period (e.g., Fourteen Mile Creek at Lakeshore Rd; Bronte Creek upstream of Mountsberg Reservoir and Grindstone Creek at Hamilton Harbour). Concentrations are influenced by erosion and soil type. Other factors that can increase concentrations include fertilizer application, runoff from poorly managed fields, increased impermeability of soils in urban areas that increase stormwater runoff, loss of riparian vegetation that filter and store nutrients, municipal wastewater, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors total phosphorus concentrations as part of the Provincial Water Quality Monitoring Network and through our surface water quality monitoring program.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Thermal pollution occurs when surface water temperatures increase. Widespread increases in surface water temperatures have been recorded in central and downstream reaches across the watershed over the last 20 years. Surface water temperature is influenced by yearly and seasonal weather (e.g., wet versus dry, air temperature, etc.), sun exposure, creek channel form, groundwater discharge, and erosion (e.g., wider, shallower creeks with more surface area). Other factors can increase surface water temperature including increased impermeable surfaces and reduced natural shade in urban areas, loss of forests and riparian vegetation, use of dams and on-line ponds which increase surface exposure to sunlight, surface water takings which temporarily reduce water depth, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors surface water temperatures through our surface water quality monitoring program.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
|
Description: Groundwater is the water that infiltrates the soil, is stored, and moves underground. Private and municipal groundwater wells serve approximately 12% of Conservation Halton’s watershed population. The number of municipal drinking water system users is increasing. Groundwater quantity is influenced by the size of aquifers which are bodies of rock and/or sediment that hold groundwater, the ability of the materials in the ground to transmit water, and the loss and gain of water (water balance). Other factors can decrease groundwater quantity, including increased groundwater demand and excessive pumping, increased impermeability of soils due to urbanization, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors groundwater quantity through the Provincial Groundwater Monitoring Program and at selected wetland locations.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Groundwater quality is the physical, chemical, biological, and radiological characteristics of water under the earth’s surface. Water quality is described by measuring key characteristics or indicators such as chloride, sodium, nitrate, sulphate, arsenic, iron, lead and manganese. Groundwater quality varies across the watersheds but is generally good quality. However, some areas show trends of increasing chloride and sodium concentrations in well supplies. Groundwater quality is influenced by the permeability and chemical properties of the rocks and sediments through which it moves, the depth from ground surface, and natural climatic variations (e.g., rainfall and evaporation rates). Other factors can worsen water quality including the use of road salt and water softening salt, application of fertilizers, runoff from poorly managed fields, septic system effluent, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors groundwater quality indicators as part of the Provincial Groundwater Monitoring Network and through our groundwater quality monitoring programs.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Natural features include forests, wetlands, valleys, and water courses. They provide benefits and services such as flood attenuation, erosion control, carbon storage, filtration of contaminants, wildlife habitat, recreation, and more. In Conservations Halton’s watersheds, over 70% of wetlands have been lost or fragmented; remaining wetlands are located primarily in the upper watershed reaches. Riparian habitat coverage is variable but poor overall, especially in highly urbanized areas. Forest cover is poor overall. Large tracts of forest are rare (mostly above the Niagara Escarpment) and urban forests are small. Degradation, fragmentation, and loss of natural features are influenced by yearly and seasonal weather patterns, natural hazards (e.g., erosion, flooding and drought), and disease. Other factors can worsen degradation and loss including the removal of natural features and wildlife corridors, urban encroachment, invasive species (e.g., emerald ash borer), linear infrastructure (e.g., roads, utilities, etc.), and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors biodiversity and ecological health through our Long-Term Ecological Monitoring Program (LEMP). Trends are monitored through our Ecological Land Classification (ELC) and Natural Areas Inventories.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Invasive species (e.g., emerald ash borer and garlic mustard) are organisms that are not native to an area, adapt easily, reproduce quickly, and have a broader tolerance for a range of environmental conditions than native species. Natural features across Conservation Halton’s watershed, such as forests and wetlands, are negatively affected by invasive species. They are spread naturally by vectors such as wind, animals, insects and birds, and extreme weather events (e.g., hurricanes and flooding). Other factors can increase the spread including human activity (e.g., deliberate or accidental introduction of invasive species such as zebra mussels, goldfish, and purple loosestrife), and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors the existence, spread and impact of invasive species.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Description: Biodiversity loss is the decrease or disappearance of species. The status, health, and range of many species is shifting in Conservation Halton’s watersheds (e.g., decline of some tree species due to pests/pathogens). Biodiversity loss is influenced by yearly and seasonal weather patterns, natural hazards (e.g., erosion, flooding, and drought), and disease. Other factors that worsen biodiversity loss include loss of natural features and habitat, habitat degradation and fragmentation, spread of invasive species, and climate change.
Conservation Halton monitors biodiversity through our Long-Term Ecological Monitoring Program (LEMP) and Natural Areas Inventories.
| VULNERABLE AREAS | KEY IMPACTS |
|
SOCIO-ECONOMIC:
|
Public Survey Results
A public consultation period from 10月 27 to 12月 8, 2023 engaged local municipalities, members of the public, and others who live and work within Conservation Halton’s watersheds to share their insights and opinions about key natural resource issues in our jurisdiction.
The 159 survey submissions confirm that our proposed key issues reflect local concerns and priorities. Responses provided further examples of where key issues are a concern and identified groundwater quality as a missing key issue. Public feedback has been incorporated into the Summary of Key Natural Resource Issues.
Survey participants identified the following issues as the most important:
- Degradation, Fragmentation & Loss of Natural Features
- Groundwater Quality
- Biodiversity Loss
- Riverine Flooding
- 入侵物种
Groundwater Quality has been added to our summary of key issues. Other identified concerns (e.g., air quality, protection of archeological sites, noise pollution) are beyond the scope of the Watershed Strategy because they are within the mandate of other groups and agencies.
Survey participants identified five watershed monitoring priorities:
- To coordinate monitoring efforts with municipalities and others to avoid duplication
- To focus on identifying trends based on good data, and to share data and information regularly
- To identify and fill data gaps with a focus on understanding the key watershed-scale natural resource issues
- To identify natural assets on a watershed basis, and
- To collect and assess data to inform management actions and outcomes (adaptive management)
Survey participants agreed that Conservation Halton should continue to build partnerships and recommended that partnerships focus on:
- Coordinating activities, particularly with respect to climate change initiatives
- Exploring opportunities for additional program funding and in-kind support
- Hosting a shared repository of monitoring data, natural heritage information and restoration opportunities
- Undertaking Lake Ontario shoreline monitoring and management
- Promoting volunteer opportunities (e.g., citizen science/community explorers)
- Fostering and facilitating landowner stewardship activities
Several survey participants recommended that Conservation Halton take a lead role, among partners, in assessing the impacts of climate change on local natural resources and determining their value as natural assets at the watershed scale.
City of Burlington. Story Map: Climate Change Impacts. Accessed 七月 13, 2023.
Conservation Halton. 2002. Bronte Creek Watershed Study.
Conservation Halton. 2006. Northshore Watershed Study.
Conservation Halton. 2017. Water Quality in the Conservation Halton Watershed: 1964-2014.
Conservation Halton. 2018. Watershed Report Card.
Conservation Halton. 2018. Story Map: Terrestrial Monitoring.
Conservation Halton. 2018. Story Map: Aquatic Monitoring.
Conservation Halton. 2021. Story Map: How Much Habitat is Enough?
Conservation Halton. 2021. Story Map: Water Quality.
Conservation Halton, 2022. Water Temperature Data Analysis.
Conservation Halton. 2022. Story Map: Monitoring Watershed Health.
Conservation Halton. 2023. Watershed Report Card.
Environment and Climate Change Canada. 2019. Canada’s Changing Climate Report.
Gore and Storrie Limited and Ecoplans Limited. 1996. Sixteen Mile Creek Watershed Plan.
Halton Region. 2020. Climate Change Discussion Paper, Regional Official Plan Review.
Halton Region Conservation Authority. 1983. Interim Watershed Plan.
Halton Region Conservation Authority. 1998. Grindstone Creek Watershed Study.